ICYMI, batteries are the new black when it comes to clean energy. Power grids across the country are stressed by summer heat waves that are baking most American cities. What’s cushioning against rolling blackouts and keeping the AC humming is battery storage. No, not the Duracel kind, but the kind that sits under the hood of your nearest Chevy Bolt or is standing by to power your home or local hospital in the event of a blackout.
By 2025, 13 battery factories are expected to be in operation across the U.S. Global battery storage brands like Panasonic Energy, Samsung, and LG Energy Solutions are choosing to build new gigafactories in Nevada, Tennessee, and Kansas, with more factory announcements on deck. Additionally, U.S. car makers are building battery plants largely located in the American Southeast to meet the anticipated 22 million electric vehicles on U.S. roads by 2030. EVs may be the popular focus for sourcing and building batteries in the U.S., but there are many other ways batteries are ushering in our clean energy future.
Solar installations are climbing in number throughout the United States and increasingly reliant on battery storage. When the sun beams down on a home, business, or other solar installation, a large amount of energy is generated. Some of that juice might get used immediately, but without an efficient storage system in place, any surplus power tends to be wasted.
On a local scale, excess power can now be stored in power banks built into a home or business. Any energy that isn’t immediately used is funneled into batteries that hold the charge until it is needed. Some systems are designed to provide power uniformly, day and night, while others have added backup capabilities that save energy for emergency situations.
For a single-family home or small business, a solar + storage system eliminates the need for a gas-powered generator for backup power. A home or business could become independent of the energy grid entirely, given adequate solar power generation and sufficient battery storage solutions.
Energy Resilience is Contagious

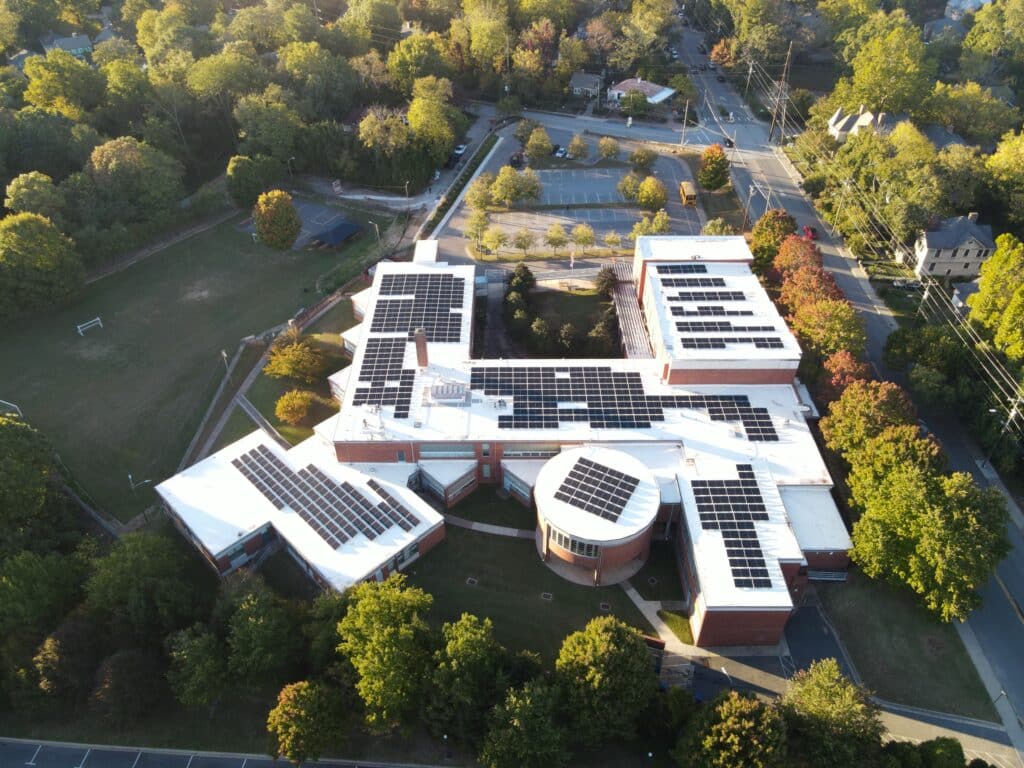
What if instead of a single home benefiting from battery storage, an entire community could reap the rewards? It’s already happening across the United States and abroad, with schools and hospitals being the first to embrace solar power storage on a scale that can make a real difference.
In some cases, these institutions act as emergency centers in their communities, providing power and stability during outages and other disruptions. This largely reduces their reliance on fossil fuels to provide backup power via generators, which is a big win for both their wallets and the planet.
Tesla powerwalls are being used in California during wildfire-caused blackouts. The new Ford F-150 Lightning is touted to power your home during a power shutoff and large U.S. cities like Miami and Los Angeles are reaping the double rewards of an electric bus fleet that runs on clean energy, doesn’t emit pollution, and is designed to support climate resiliency risks. Essential public services, like schools and hospitals across the country, are using batteries to provide safe, resilient community spaces when needed.
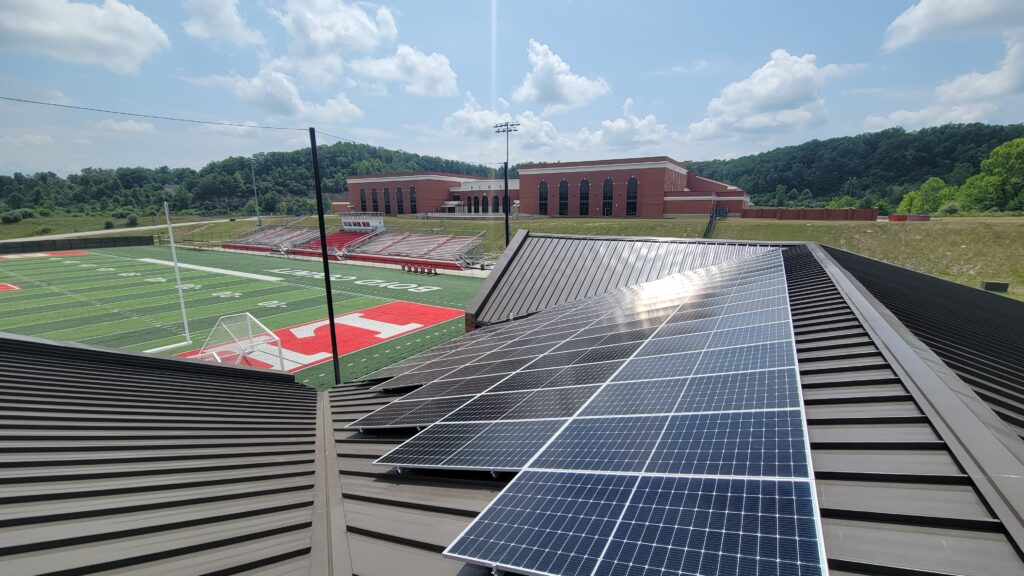
At Hopewell Valley Central High school in New Jersey, a large rooftop solar array and a larger parking lot solar canopy generate 876 kilowatts of power, meeting the school’s energy needs and charging a one-megawatt, 500kWh lithium-ion battery system. In the event of a widespread power outage, the school becomes a climate-controlled lifeline for the community, with full lighting and food refrigeration.
In places like Santa Barbara, California, schools are becoming the centerpiece of energy resilient communities, with solar + storage microgrids at a half dozen locations, for a combined 6 MWh of energy storage. These new projects are especially important in places like California that, in recent years, have dealt with the devastating effects of wildfires. By placing energy storage in areas with a low risk of fire spread, they can serve as safe havens and community shelters as extreme weather events continue.
An even more impressive project is underway in Albuquerque, New Mexico. Atrisco Heritage Academy High School is getting a massive solar makeover, with over 2,200 solar panels and a Tesla Megapack two battery storage system with a capacity of 2,884 kWh. The school, which is the largest in the state, will be well-equipped as a regional power shelter, making it the go-to for community care in a future emergency.
Hospitals are another place where solar + storage is a gamechanger. In Hawaii, Kona Community Hospital is using battery storage to keep its lights on and doors open to those in need during hurricanes and other natural disasters. The next time a severe storm rolls through and wipes out their power, their battery storage system provide backup power, ensuring that they can continue to offer vital services to their patients.
Better Technology, Lower Costs
The trend toward battery storage is being driven by a number of factors. First, the cost of high-capacity batteries has dropped dramatically in recent years, making them more affordable for both businesses and homeowners. Battery storage costs are expected to keep declining rapidly for the next decade before leveling out, according to a report from the National Renewable Energy Laboratory.
Projects that were once cost-prohibitive are now being funded more easily by public and private investment. In some cases, schools and hospitals can be equipped with solar+storage with no upfront cost by leveraging third-party financing, such as through a power purchase agreement (PPA) with a local energy company. Batteries have also become much more efficient. Simply transitioning to a lithium-ion battery that converts electrical energy into chemical energy allows more energy storage than a traditional lead acid battery.
Powering the Future
While solar has seen exponential growth for over a decade, new battery storage installations are expected to spike beginning in 2022. Overall, 60 percent of the estimated 85 gigawatt increase in U.S. power grid capacity in 2022 and 2023 is expected to come from new solar and battery storage projects, with wind power contributing a further 18 percent and fossil fuels making up the remainder.
As the electric grid becomes more decentralized, with more schools, communities, and homeowners turning to clean power, the need for energy storage will only increase. The energy storage industry is preparing to meet this demand as it grows in both size and lobbying power.
With falling prices, increasing efficiency, and advances in technology, more businesses and homeowners are pairing solar with battery storage. This pairing is the perfect match to deliver the reliability and stability that the grid of a clean energy future demands.